What is Ptosis?
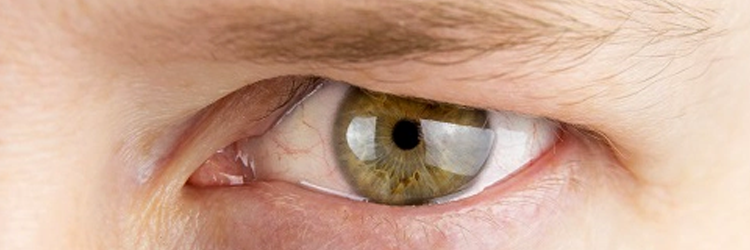
Ptosis is a condition where the upper eyelid is lower than its normal position. Also known as eyelid drooping, this condition can occur in one eye (unilateral) or both eyes (bilateral). Mild ptosis may only cause an aesthetic issue, but in severe cases, it can limit the field of vision and negatively affect daily life.
So, how can you tell if you have eyelid drooping? Here are the signs of ptosis and things to watch out for!
Symptoms of Ptosis (Eyelid Drooping)
✅ 1. Drooping of the Upper Eyelid
• The most noticeable sign of ptosis is when the upper eyelid is lower than normal.
• The eyelid may cover part of the iris (colored part of the eye) or the pupil.
✅ 2. Restricted Field of Vision
• If ptosis is severe, the eyelid may block the field of vision, making it difficult to see clearly.
• Patients may try to see better by raising their eyebrows or tilting their heads backward.
✅ 3. Constant Eyebrow Raising Reflex
• Ptosis patients may continuously raise their eyebrows to widen their field of vision.
• This habit can lead to forehead wrinkles and muscle fatigue over time.
✅ 4. Tilting the Head Back and Neck Pain
• When the eyelid obstructs vision, patients may tilt their heads backward to see better.
• This habit can lead to neck and back pain over time.
✅ 5. Eye Fatigue and Dryness
• Ptosis patients may experience eye fatigue because they exert extra effort to see.
• If the eyelid doesn’t close at its normal level, eye dryness and irritation can occur.
✅ 6. Asymmetric Eyelid Appearance
• In patients with unilateral ptosis, there is a noticeable asymmetry between the eyelids.
• One eye may appear more open, while the other appears more closed.
✅ 7. Sensation of Heaviness in the Eyes
• Ptosis can strain the eyelid muscles, causing a feeling of heaviness in the eyes.
• This sensation may increase throughout the day, making the person feel tired.
If any of the above symptoms are present, it is recommended to consult an ophthalmologist for a detailed examination.
How is Ptosis Diagnosed?
Ptosis is diagnosed through a clinical examination by an eye doctor.
Your doctor may perform the following tests:
✔ Evaluation of the eyelid position and symmetry.
✔ Testing the function of the muscles that lift the eyelid.
✔ Visual field testing to measure how ptosis affects vision.
✔ Blood tests or neurological exams may be done to identify underlying causes of ptosis.
Especially in cases of sudden-onset ptosis, a thorough examination is necessary to rule out underlying neurological conditions.
What Causes Ptosis?
Ptosis can develop due to various factors related to muscles, nerves, or skin elasticity. Here are the most common causes:
Congenital Ptosis
• Ptosis present from birth.
• It occurs due to a developmental disorder of the levator muscle, which lifts the eyelid.
Age-Related Ptosis
• As people age, the muscles responsible for lifting the eyelid weaken.
• It usually affects both eyes.
Trauma and Eye Surgeries
• Trauma to the eyelid or damage to muscles after surgeries like cataract surgery can cause ptosis.
Myasthenia Gravis and Neurological Diseases
• Neurological diseases affecting the muscles can be a cause of ptosis.
• Nerve paralysis or tumors can also lead to ptosis.
Contact Lens Use
• Long-term use of rigid contact lenses can weaken the levator muscle.
When diagnosed with ptosis, the underlying cause should be identified, and an appropriate treatment plan should be created.
What Happens if Ptosis is Left Untreated?
⚠ It may cause narrowing of the field of vision and negatively affect daily life.
⚠ Head and neck pain, eye fatigue, and chronic discomfort may develop.
⚠ In children, amblyopia (lazy eye) can develop, leading to permanent vision loss.
⚠ Severe ptosis can cause aesthetic issues, leading to psychological and social problems.
If eyelid drooping affects your vision, consult an ophthalmologist without delay.
Ptosis Treatment Methods
1️⃣ Ptosis Surgery (Levator Muscle Repair)
✔ The procedure involves tightening the muscle responsible for lifting the eyelid.
✔ It is the most effective treatment method providing a permanent solution.
✔ It can be performed with local anesthesia in a short time.
2️⃣ Botox for Temporary Solution
✔ In mild cases of ptosis, botox injections can support the muscles.
✔ The effect lasts for 3-6 months and requires regular repetition.
3️⃣ Ptosis Glasses
✔ Special glasses with frames that support the eyelids can be used in patients not suitable for surgery.
✔ It is especially recommended for ptosis caused by neurological diseases.
To determine the most suitable treatment for you, it is important to consult with your doctor.
Conclusion: How to Recognize the Symptoms of Ptosis?
Ptosis most often presents with eyelid drooping and loss of field of vision.
Eyebrow-raising reflex, head tilting, and eye fatigue are also common signs.
It can lead to complications such as amblyopia in children and head-neck pain in adults.
If untreated, it may worsen, but it can be successfully treated with surgery and botox.
If you notice eyelid drooping, contact us to determine the best treatment option for you!
Op. Dr. Yıldız Acar Ebcim
Ophthalmologist